NCTUCS 2013-Fall Introduction to Cryptography …
NCTUCS 2013-Fall Introduction to Cryptography by Professor Rong-Jaye Chen.
今天是 liuyh 講課!
Master key, Session key, X.509, PKI
- Symmetric Key Distribution Using Symmetric Encryption
- Symmetric Key Distribution Using Asymmetric Encryption
- Distribution Of Public Keys
- X.509 Certificates
- Public-Key Infrastructure
Symmetric Key Distribution Using Symmetric Encryption
加密:public key or private key
簽章:private key
symmetric key: 速度較快
asymmetric key: 速度較慢

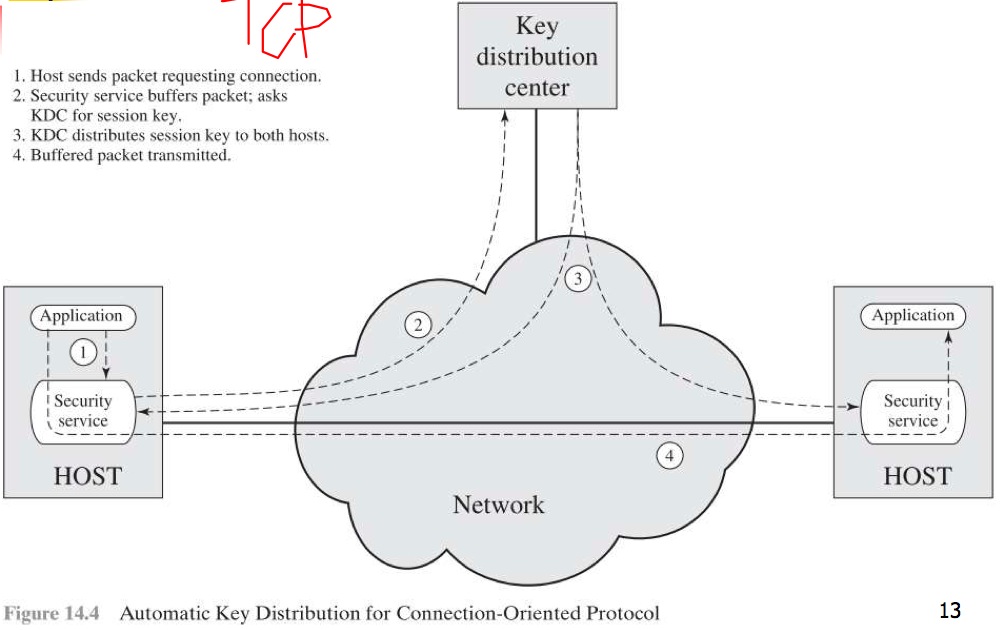
現今網路環境使用上圖的 Option 4
KDC = Key Distribution Center
Session Key => 加密 Communication
Master Key => 加密 Session Key
只需要 N 個 Master Key
Data => 有加密
Session Key => 有加密
Master Key => 沒加密
Key Distribution 的步驟
Hierarchical Key Control
- Single LAN
- KDC 和 KDC 之間有自己的方法作訊息交換
- 把 KDC 切開的好處:當某個 KDC 出事時,影響範圍較小
Session Key Lifetime
- Session Key 換的越頻繁,則越安全。
- 但一直交換 Session Key 也會造成 Overhead
- 所以要在換與不換之間找到平衡點
- 如果 Connection 會進行很長的一段時間
- 傳輸過程會跟資料及封包的格式有關
- UDP => connectionless => 一個連線不太需要換 Session Key
=> 改成每次交換都用新的 Session Key => 不符合 connectionless 需要快速的原則
=> 改用有時效性的 Session Key 會是比較好的作法
A Transparent Key Control Scheme
Decentralized Key Control
- Fully Decentralized => 每個 host 兩兩之間都會有一個 Master Key => 沒有中央化的存在
- 缺點: N 個 hosts 需要 N(N-1)/2 個 Master Key => 又回到了原本的數量級
- 優點: 較安全
Controlling Key Usage
如果把 Master Key 當成 Session Key 來用的話,在安全性上可能會洩漏用該 Master Key 加密的 Session Key
到此為止,還是沒交代 Master Key 從何而來
Symmetric Key Distribution Using Asymmetric Encryption
- 效率較差
- 用來加密並傳輸 secret key

- 優點
- 安全性較高,Key 被破解了,只會影響該次傳輸,不會影響該次前後的傳輸。
- 缺點
- 有 Man-in-the-middle-attack 的風險
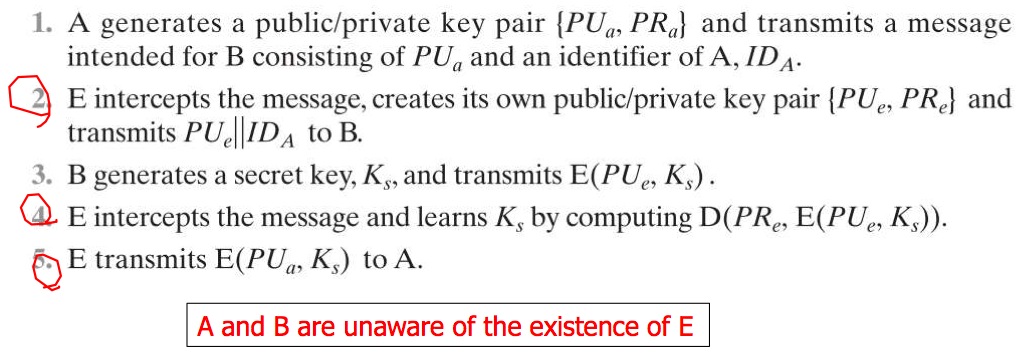
- 有 Man-in-the-middle-attack 的風險
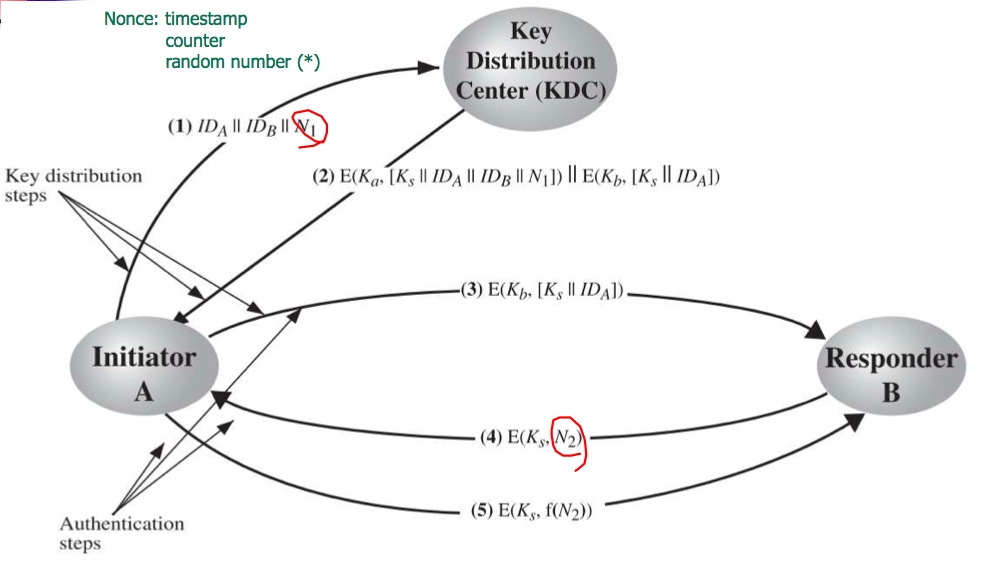
為了抵抗 Man-in-middle-attack 修改之前的方法
前提:A 和 B 必須先交換過彼此的 Public Key
1. A 將 identifier 加上 N1 再用 B 的 public key 加密,丟給 B
2. B 收到後解開,得到 N1,再把 N1 加上 N2,用 A 的 Public key 加密,丟給 A。 (證明自己是B)
3. A 將 N2 用 B 的 Public Key 加密後,丟給 B。(證明自己是 A)
4. A 將 secret key 用 A 的 private key 加密,再用 B 的 Public key 加密後,丟給 B
如此可以確定雙方都是真的 A 和 B。
A Hybrid Scheme
見投影片 p.21
Distribution Of Public Keys
Public Announcement of Public Key
- 每個人都可以假裝是別人,然後發別人的 Public Key,所以拿到的 Public Key 可能是假的。
太危險,不能用。
Publicly Available Directory
- Authority maintain {name, public key},確保 Public Key 是正確的。
- 當面或用其他可以確認的安全方法跟 Authority 註冊
- 使用者要跟 Authority 拿 Key 必須透過強制的加密連線
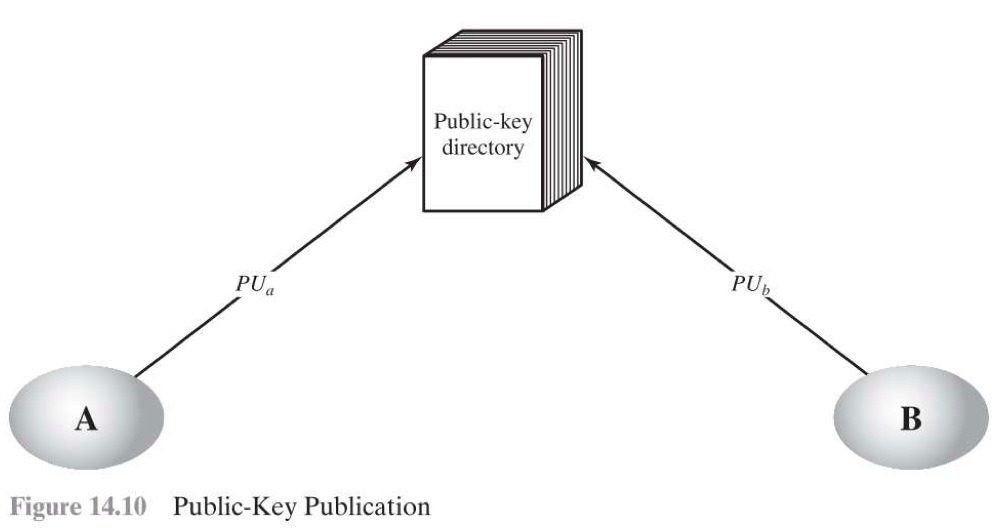
Key 仍然可能會被使用者洩漏
Public-Key Authority
- Authority 會有 Public Key 和 Private Key
- T1, T2 => Timestamp
- N1, N2 => nounce
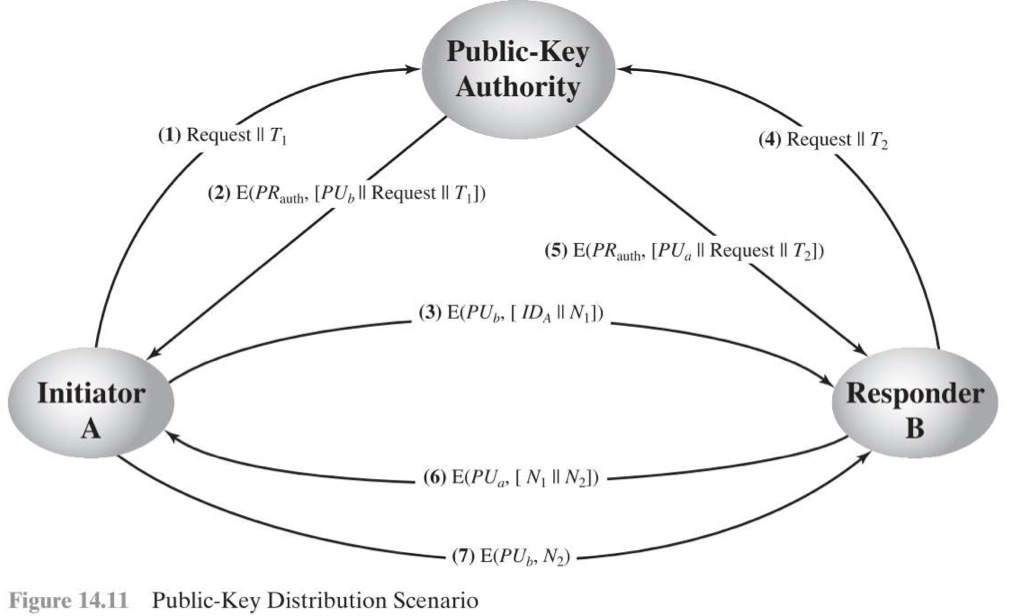
只要 Authority 被攻破,這個方法基本上就毀了。
Authority 也是 Bottleneck 的主因
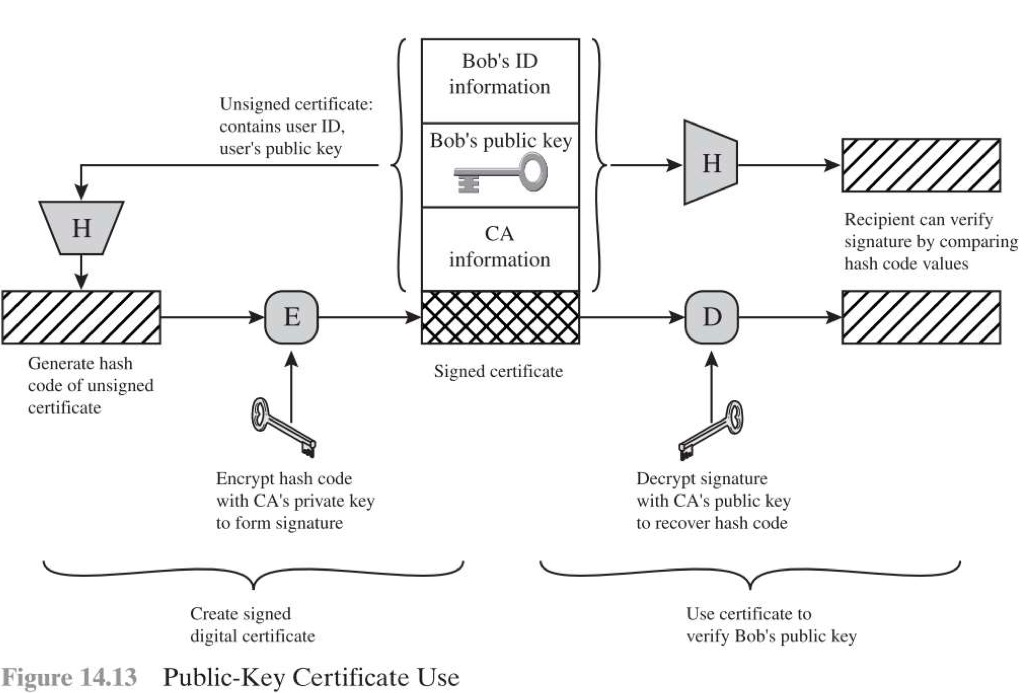
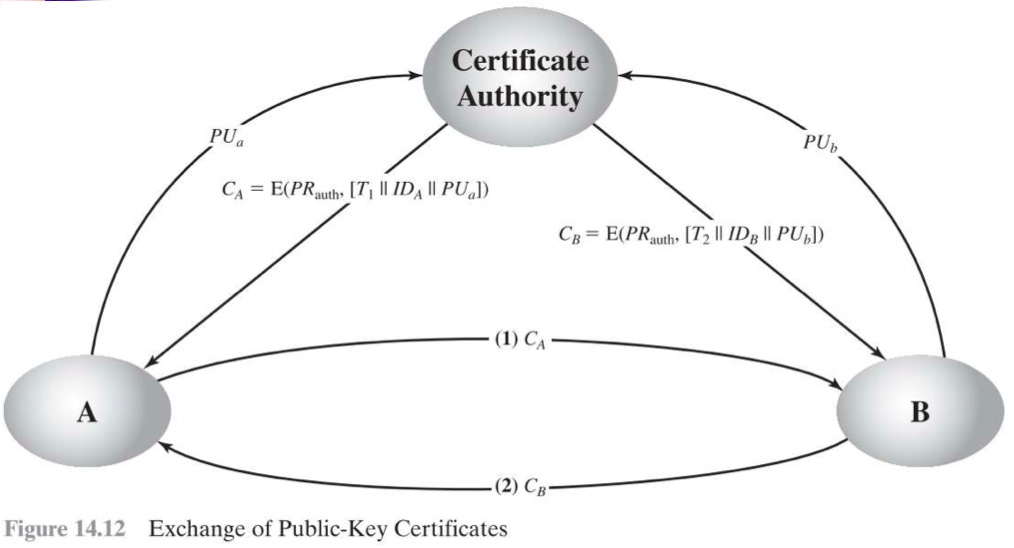
Public-Key Certificates
- 目前最常用的方法
- 1978年出現,Kohnfelder
- 直接用 certificate 讓雙方交換彼此的 key,不用透過 public-key authority
- 透過 Timestamp 可以得知此 certificate 是否已經過期

X.509 Certificates
User 的 public-key + CA 的 private-key + Hash = Certificate
X.509 的格式
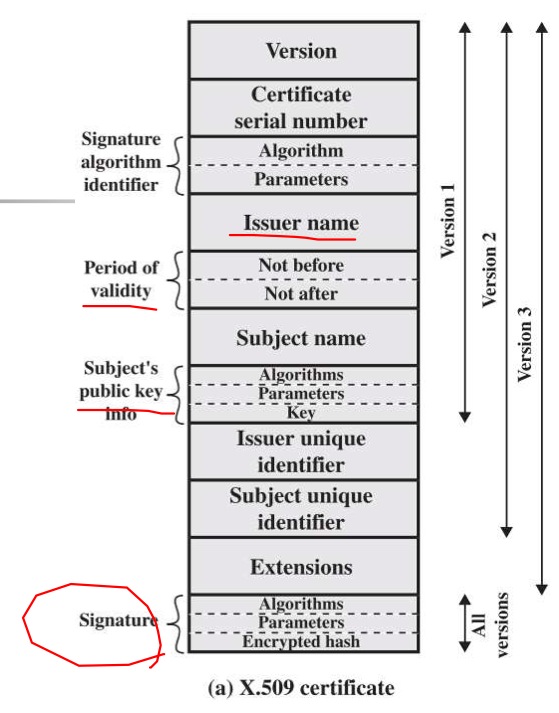
- 有分 version 1, 2, 3
- Subject Name: 這個 Certificate 是誰的
- Period of validity: 有效期間
- Issuer name: CA 的名字
- Certificate serial number: CA 給的流水號,不會重複
- Subjects's public key info: user 的 public-key 相關資訊
- Signature: CA 簽章
Y<<X>> 代表由 Y 這個 CA 簽署 X 的 public-key 的 certificate
Y<<X>> = the certificate of user X issued by certification authority Y
Obtaining a user's certificate
- 每個 User 都會相信幫其簽署 Certificate 的 CA,因此會接受所有由同一個 CA 簽署的 Certificate
那由不同 CA 簽署的 Certificate 彼此之間要如何認證?
有 X1<<A>> 和 X2<<B>> 要如何讓 A 和 B 互相信任?
for A: X1<<X2>>X2<<B>>
for B: X2<<X1>>X1<<A>>
- CA 之間彼此簽署 Certificate
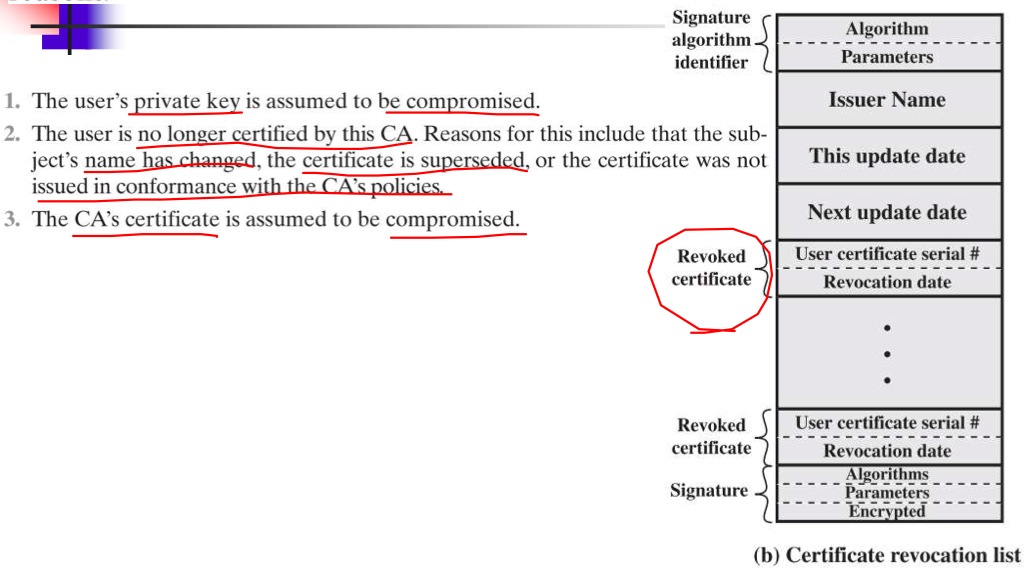
Revocation Of Certificates
- 舊的 Certificate 時間到期,必須廢除。
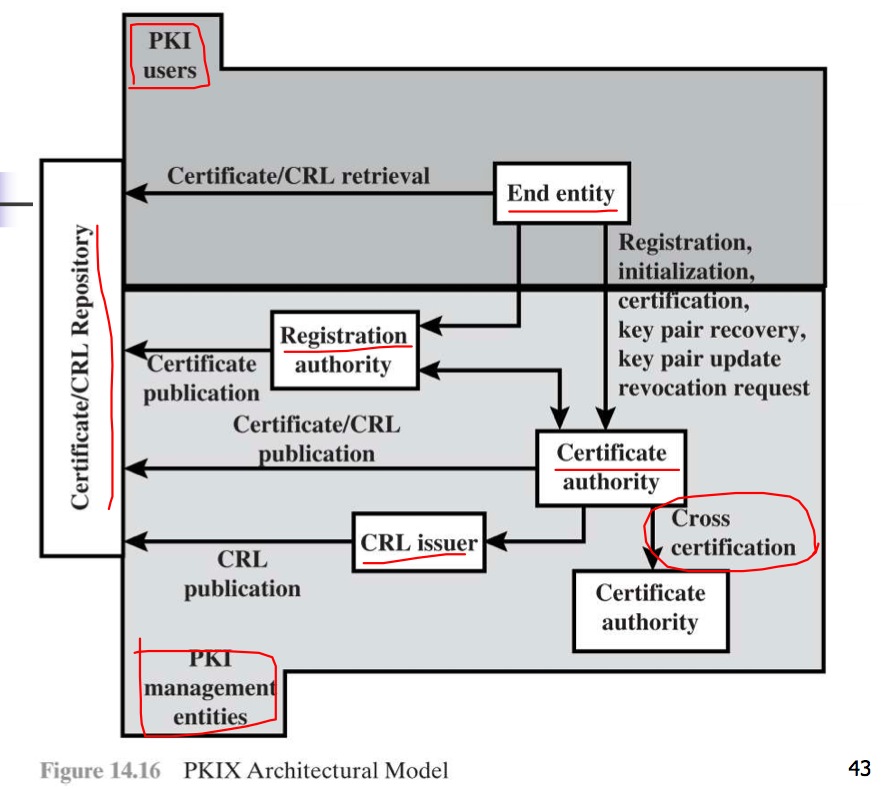
Public-Key Infrastructure (PKI)
RFC 2828, RFC 4949, RFC 5280
- PKI Users
- CA
Share
Donation
如果覺得這篇文章對你有幫助, 除了留言讓我知道外, 或許也可以考慮請我喝杯咖啡, 不論金額多寡我都會非常感激且能鼓勵我繼續寫出對你有幫助的文章。
If this blog post happens to be helpful to you, besides of leaving a reply, you may consider buy me a cup of coffee to support me. It would help me write more articles helpful to you in the future and I would really appreciate it.