Introduction to Computer Security HW1 …
Introduction to Computer Security HW1
- Select a web site.
- Use “Wget” or “Teleport Pro” to mirror the site. Look for comments within comment tags. Give screen dumps and explain what you found.
- Screen Dumps & Explanations
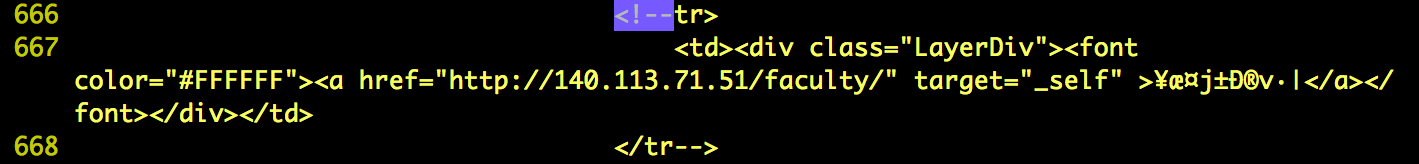
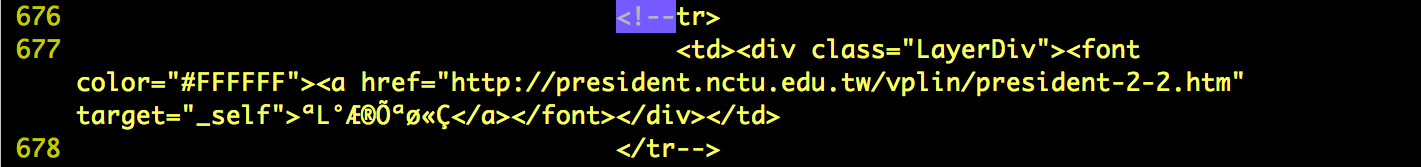
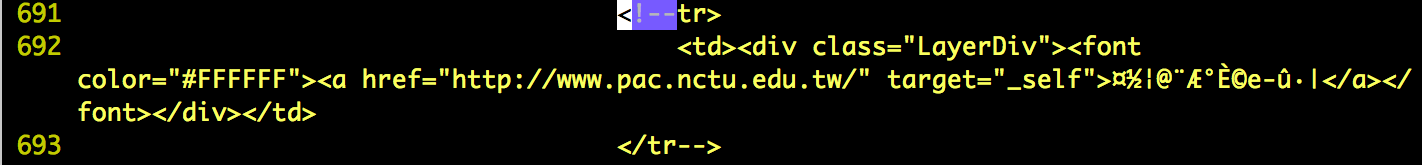
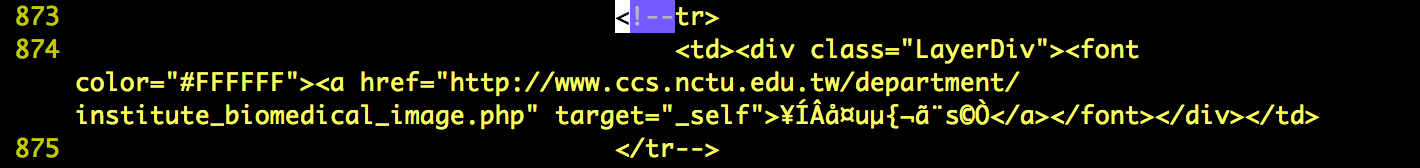
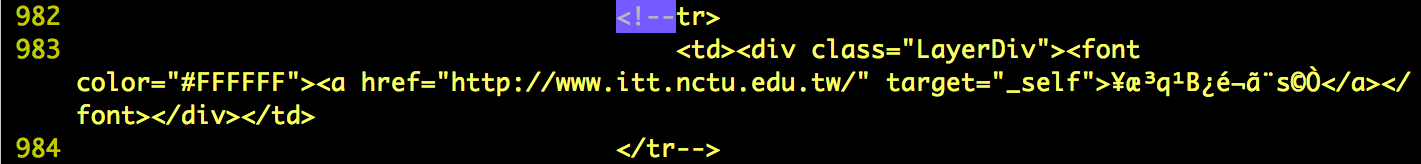
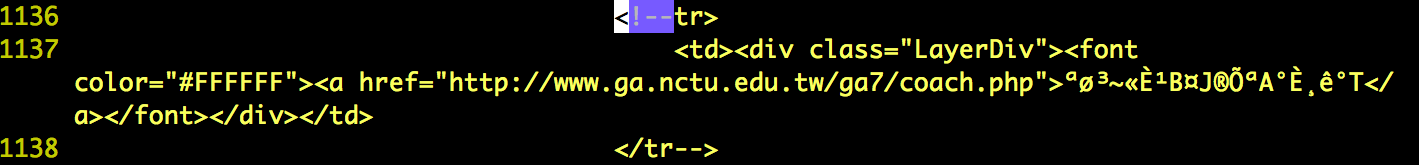
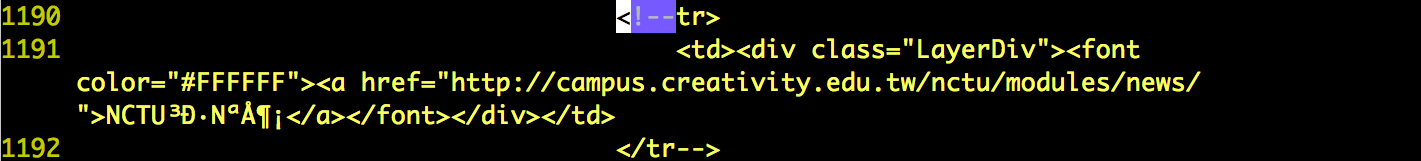
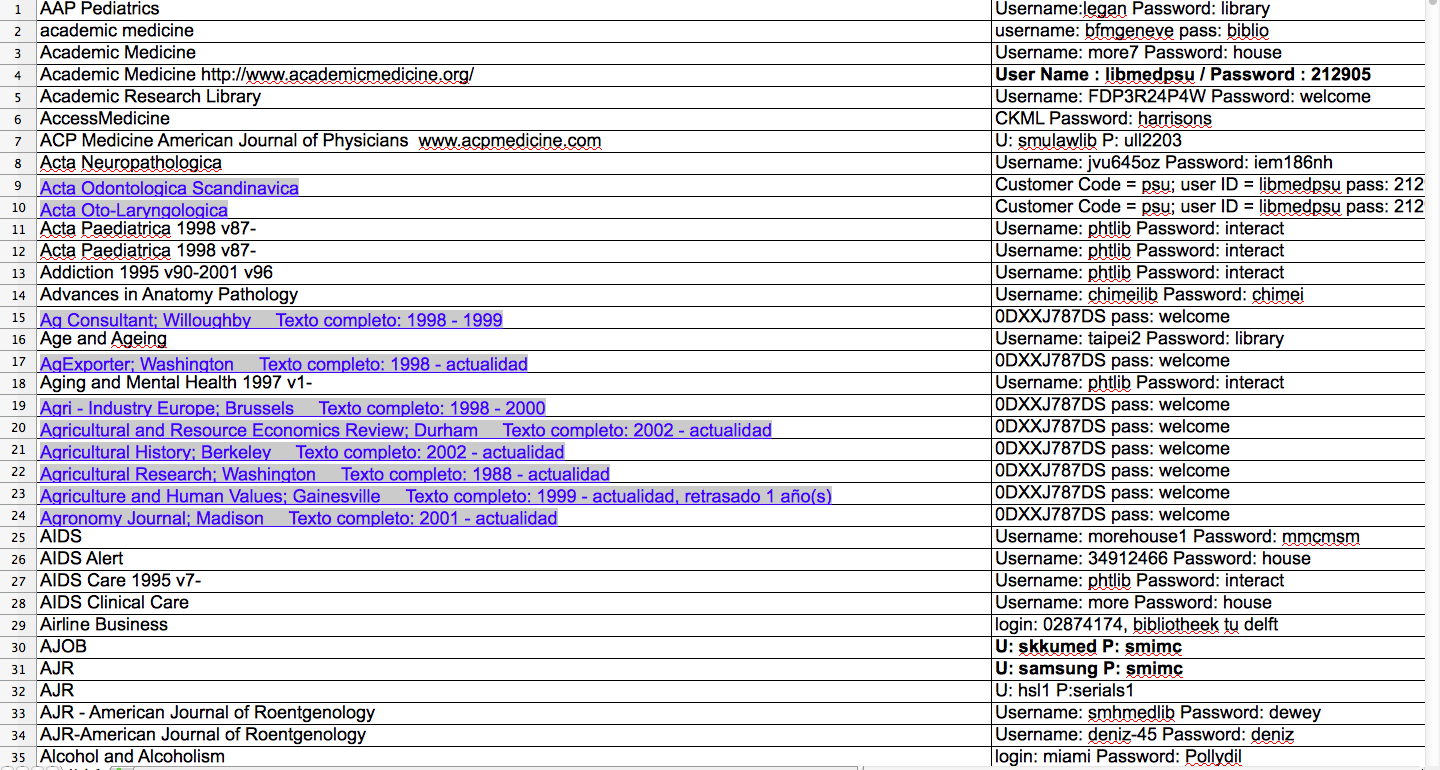
- I've found some hidden targets that not be shown on the home page of http://www.nctu.edu.tw. These website probably still working but out of date or have already be deprecated that nobody maintain the website and may have some flaws. Below is the lists.
- http://140.113.71.51
- http://president.nctu.edu.tw
- http://www.pac.nctu.edu.tw
- http://www.pac.nctu.edu.tw
- http://www.ccs.nctu.edu.tw
- http://www.itt.nctu.edu.tw
- http://www.ga.nctu.edu.tw
- http://campus.creativity.edu.tw
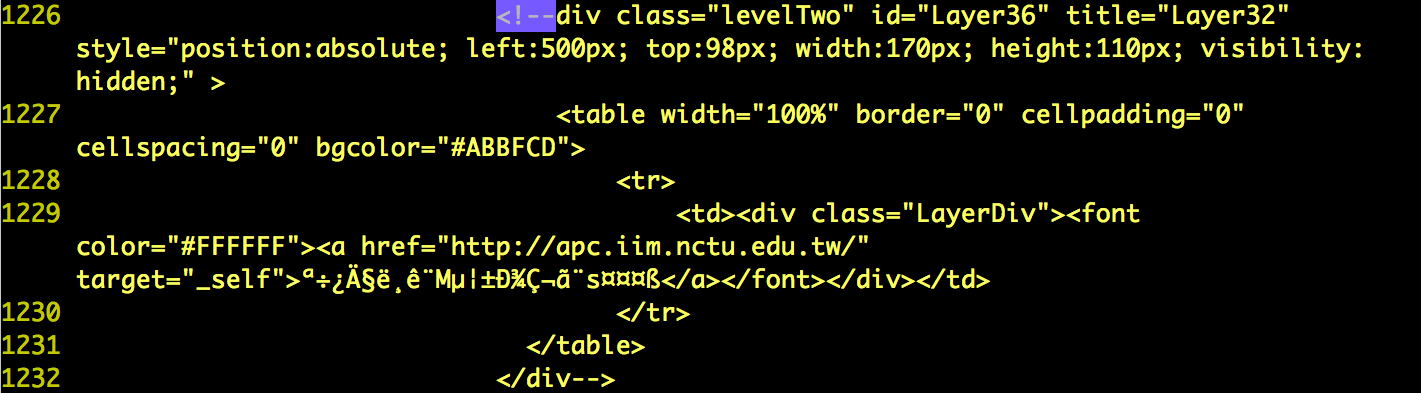
- http://apc.iim.nctu.edu.tw
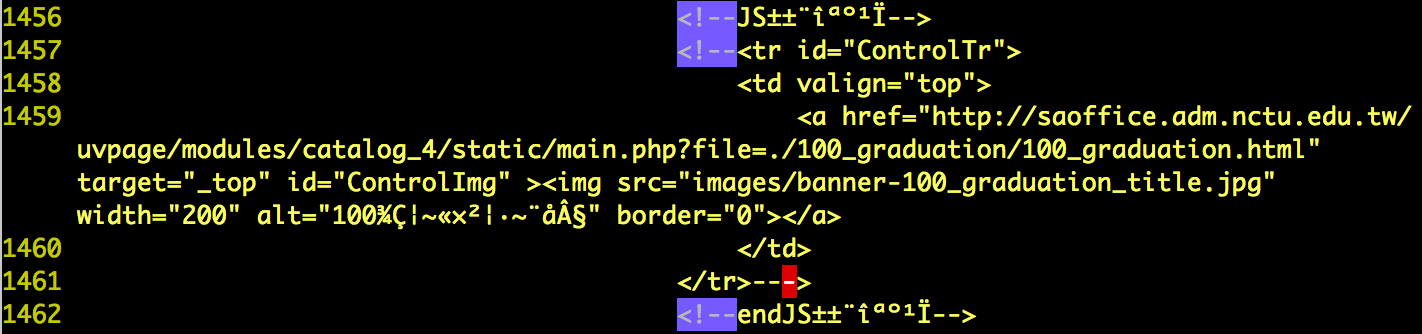
- http://saofficion.adm.nctu.edu.tw
- Screen Dumps & Explanations
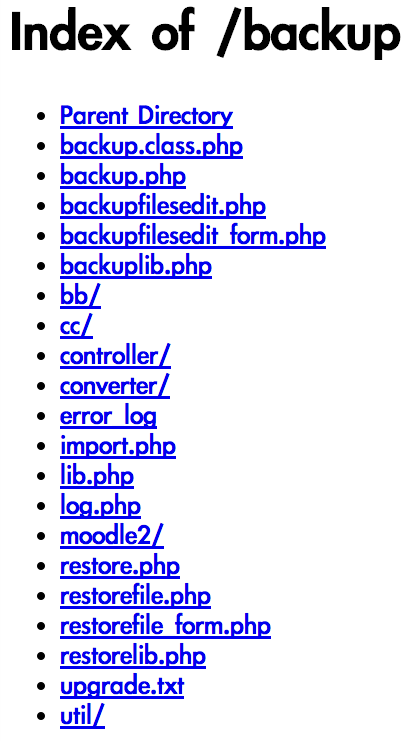
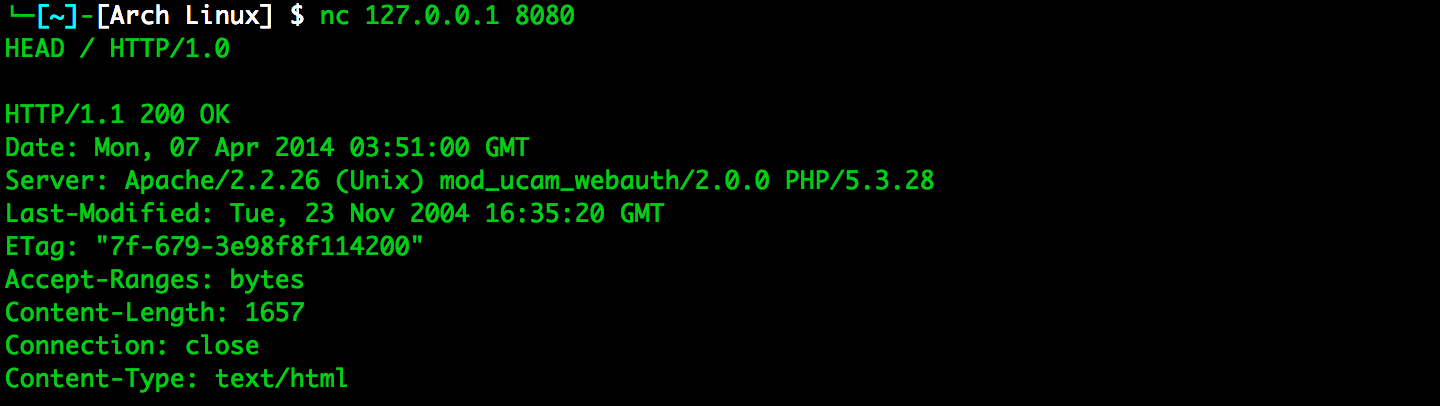
- Use “DirBuster” with a proxy feature through “privoxy” to enumerate hidden files and directories. Screen dump and explain the hidden files and directories you found.
- Screen Dumps & Explanations
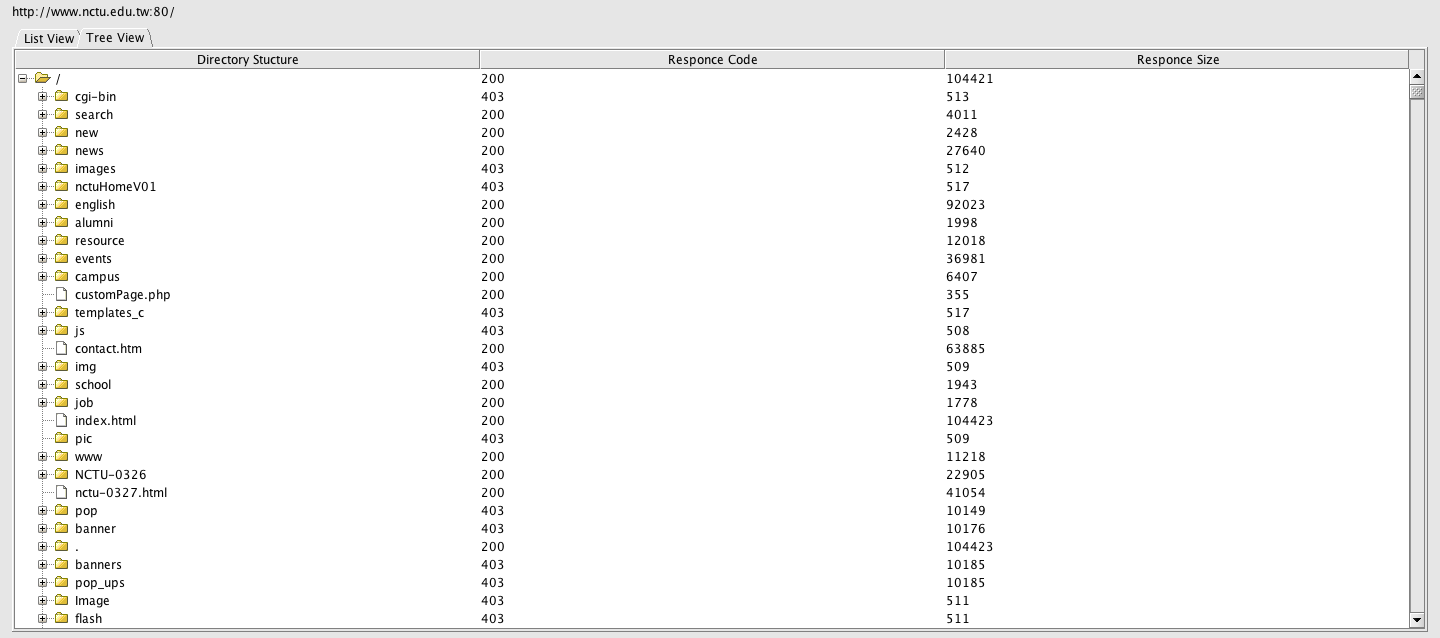

- Maybe there some something useful in these index.php files.
- Screen Dumps & Explanations
- Use “Wget” or “Teleport Pro” to mirror the site. Look for comments within comment tags. Give screen dumps and explain what you found.
- Lookup “How I met your girlfriend” in the BlackHat 2010 demo to explain, in 0.5 page, how this was done.
- Explanations
The speaker first study on the session mechanism of the Facebook.
He reduced the complexity of breaking session steps by steps.
The Entropy had be redurced from the initial 160 bits to only 20 bits!! He kept tracing the source code and hacking it.
Then, he used a techical skill called "NAT pinning" to confuse the router at protocol level.
After that, he also used the IRC bot, Geoloction via XSS and HTML5 anti-WAF XSS.
Combined all these skills and analysized based on those results.
Finally, he used the triangle localization to find someone's girlfriend in reality.
- Explanations
- Select a person. Use on-line sites for phone book, social network, information, job, photo management, business directory, jigsaw.com, etc. to summarize, with screen dumps and explanations, what information you can get. If your target is not in US nor native English speaker, you might need to use on-line sites different from the textbook.
- Screen Dumps & Explanations
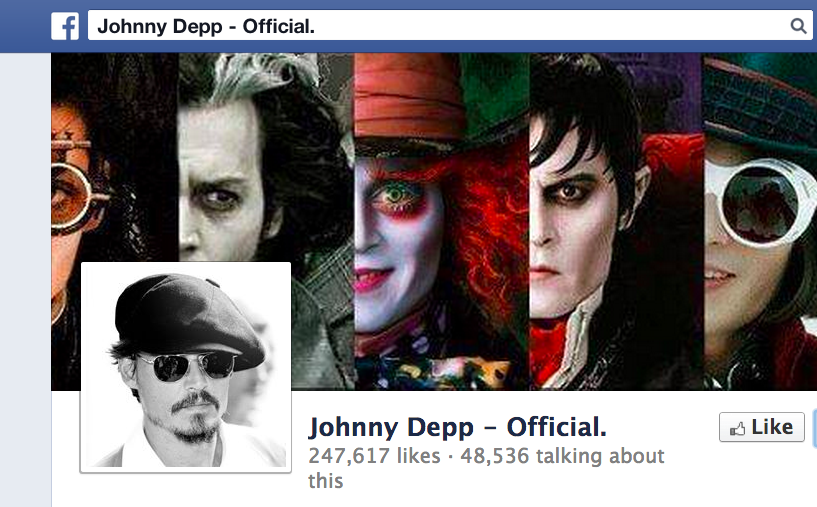
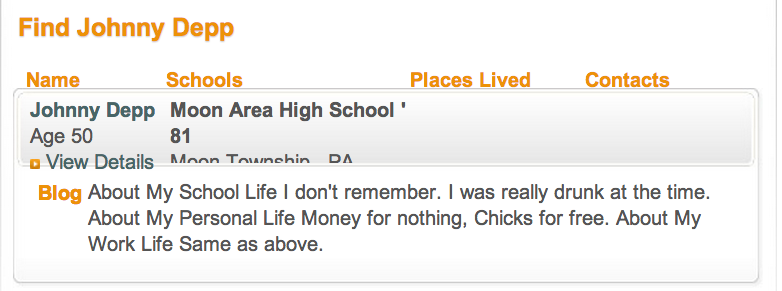
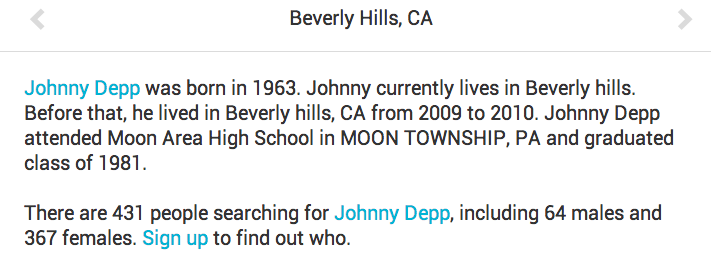
- Name: Johnny Depp (John Christopher Depp II)
- wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Johnny_Depp
- http://www.peoplesearch.com
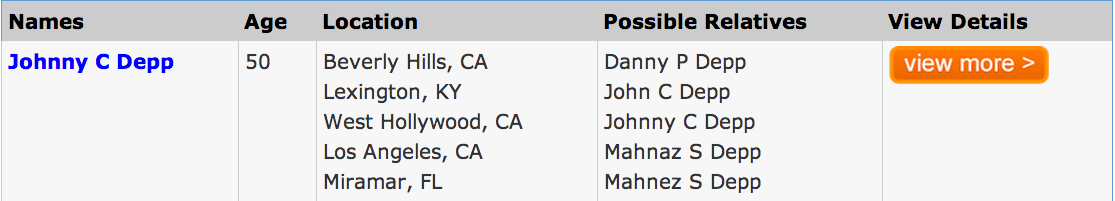
- view more need to pay some money
- https://www.facebook.com/JohnnyDepOfficial
- http://www.reunion.com/johnnydepp/
- http://www.mylife.com/mick563
- https://twitter.com/J0HNNYDepp
- Screen Dumps & Explanations
- Google “XYZ resume firewall” and “XYZ resume intrusion detection” where “XYZ” is the name of your target company. Screen dump “useful” results and explain what you got.
- Screen Dumps & Explanations


- A company called "Systems Technology International" is looking for who will use Linux iptables firewall.

- A company called "ICF International" is looking for who have experience with using Snort IDS.
- Screen Dumps & Explanations
- Lookup Archive.org and Google cached results, and select a target web site. Compare the differences between an archived and cached copy with its current on-line web site. Give screen dump and explain the differences.
- Screen Dumps & Explanations
- Archive.org
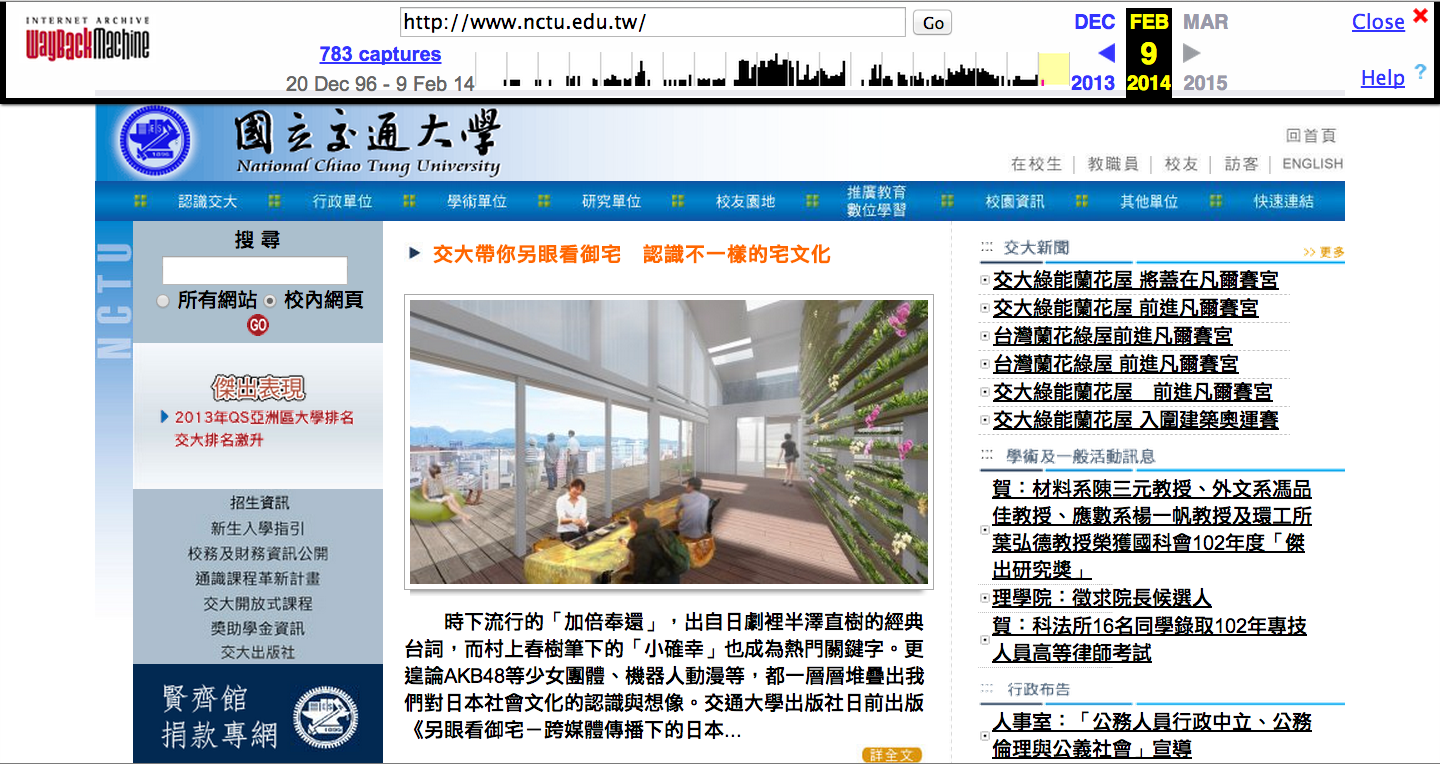
- 2014/02/09
- Google cached
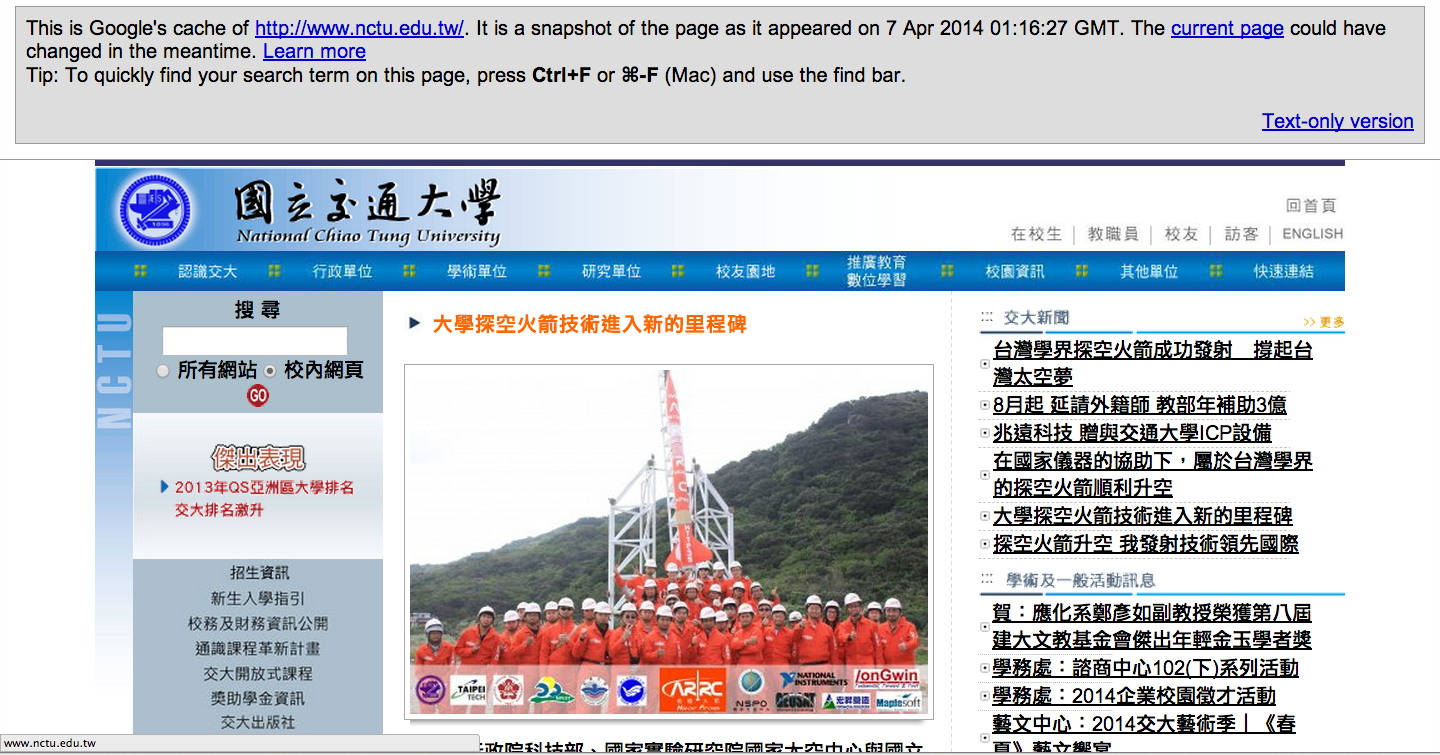
- 2014/04/07 01:16:27 GMT
- current
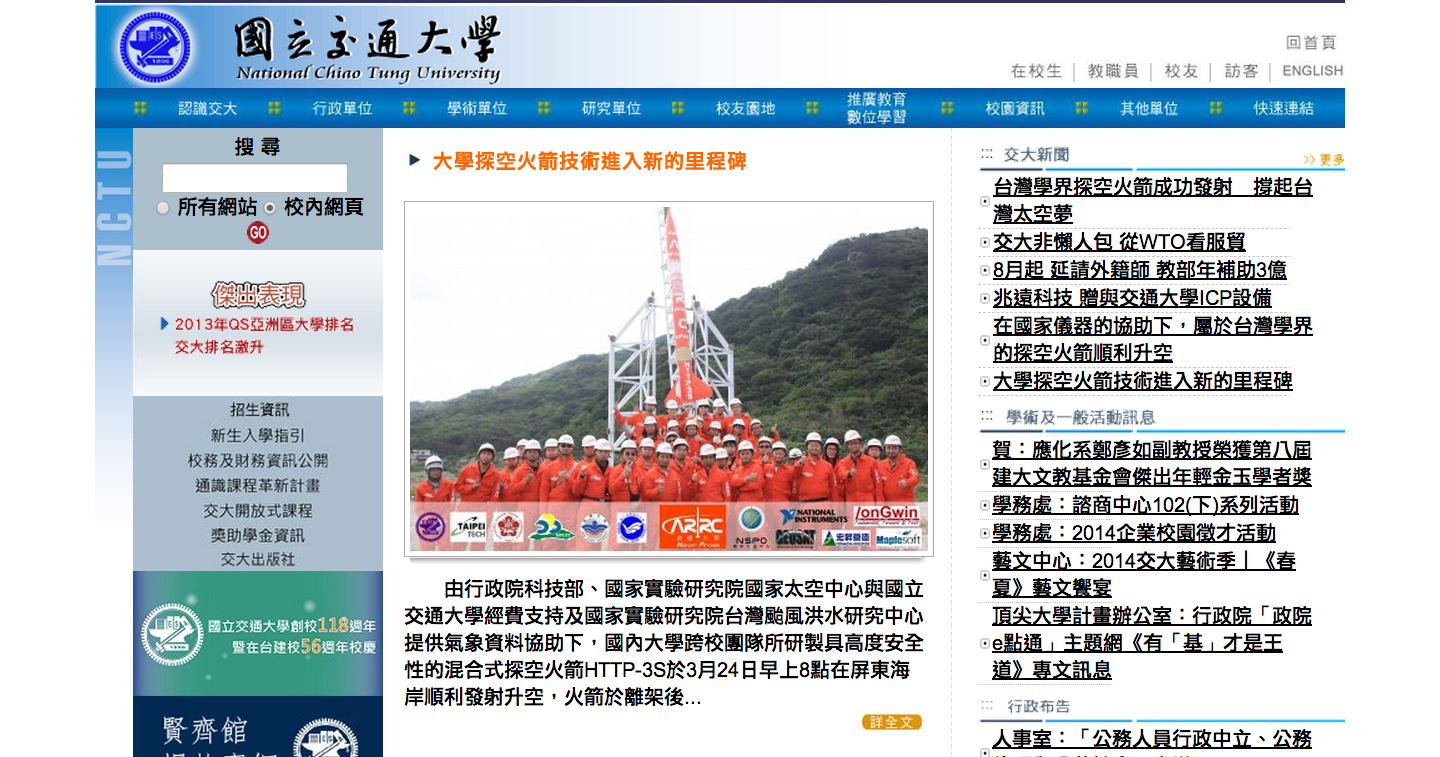
- 2014/04/07 09:00:03 GMT
- Archive.org have older information. Google cached seems no different from the current website because the cached information just few hours ago.
- Archive.org
- Screen Dumps & Explanations
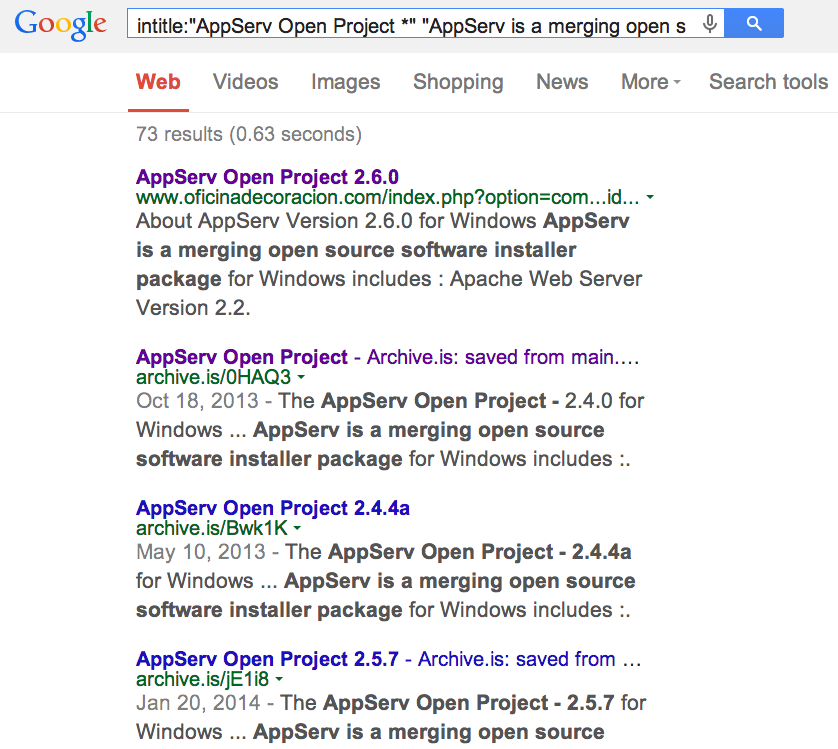
- Find Google Hacking Database at hackersforcharity.org/ghdb/. Summarize what it has and select 3 strings to search. Screen dump and explain what you got.
- What GHDB has
- it store the google search sentences which can be used to search some specific websites vulnerabilities. There are many entries and each entry have many google search sentences for searching vulnerabilities. The information on the GHDB maybe too old. The newest record is almost eight years ago (2006), though it seems still working...
- Screen Dumps & Explanation
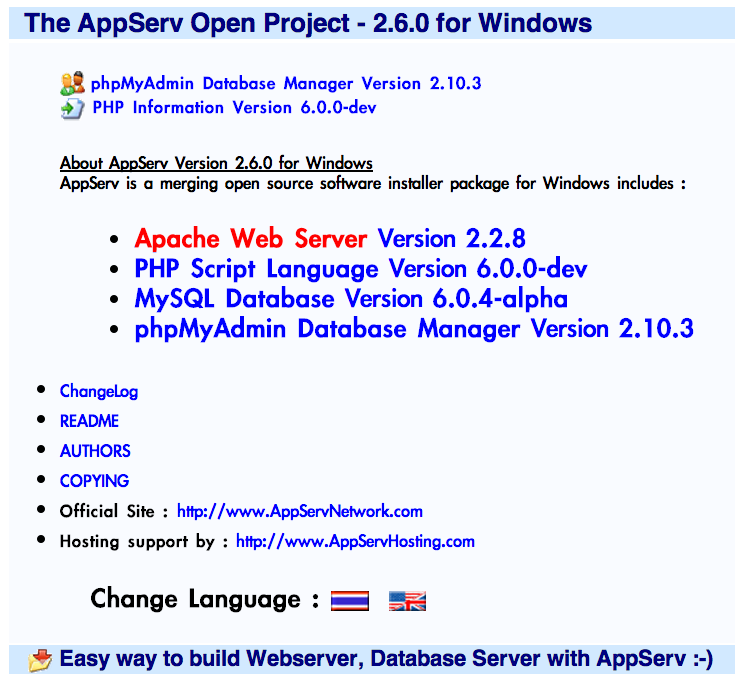
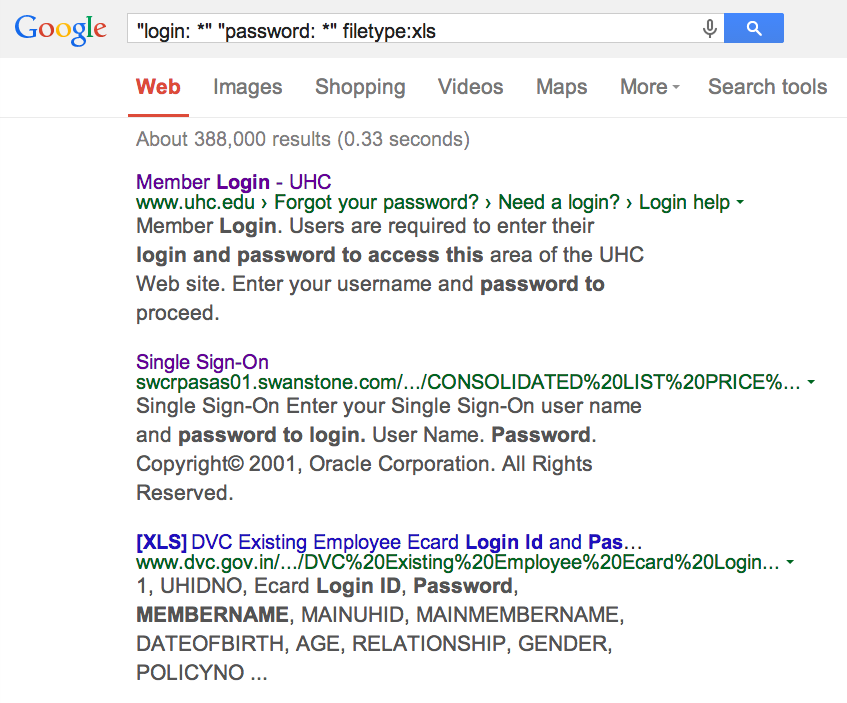
- Juicy information of the websites built by AppServ
- .xls files within user id and password
- backup directories of the server
- Juicy information of the websites built by AppServ
- What GHDB has
- Select a web site. Start from whois.iana.org to find its registry, registrar, and registrant. Also select an IP address. Start from arin.net to find who owns the IP address. Show your screen dump and explain.
- Screen Dumps & Explanations
- whois.iana.org - www.nctu.edu.tw
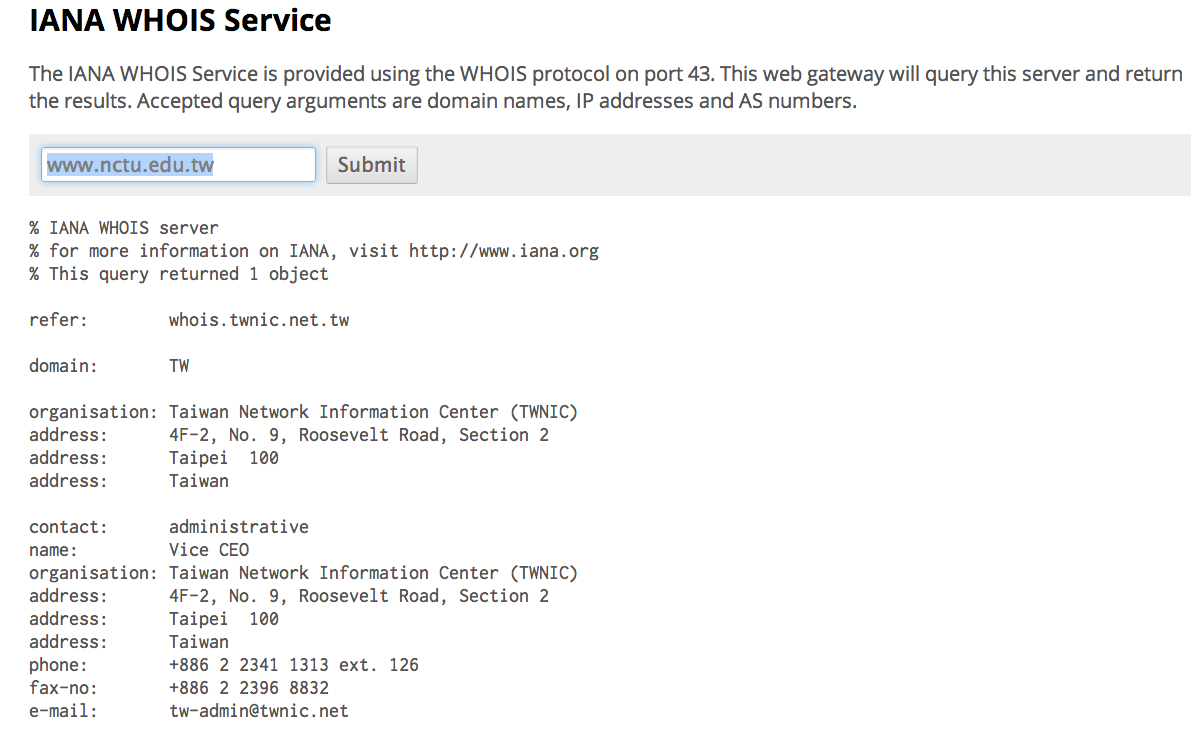
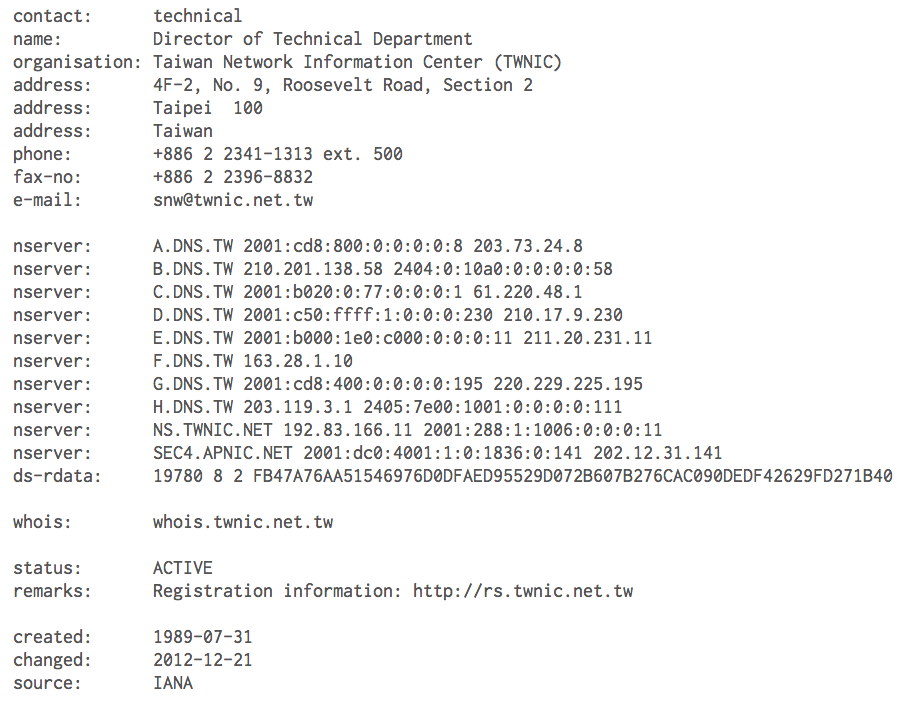
- Registry: Taiwan Network Information Center (TWNIC)
- Registrar: rs.twnic.net.tw
- Registrant: Vice CEO
- arin.net - 8.8.8.8
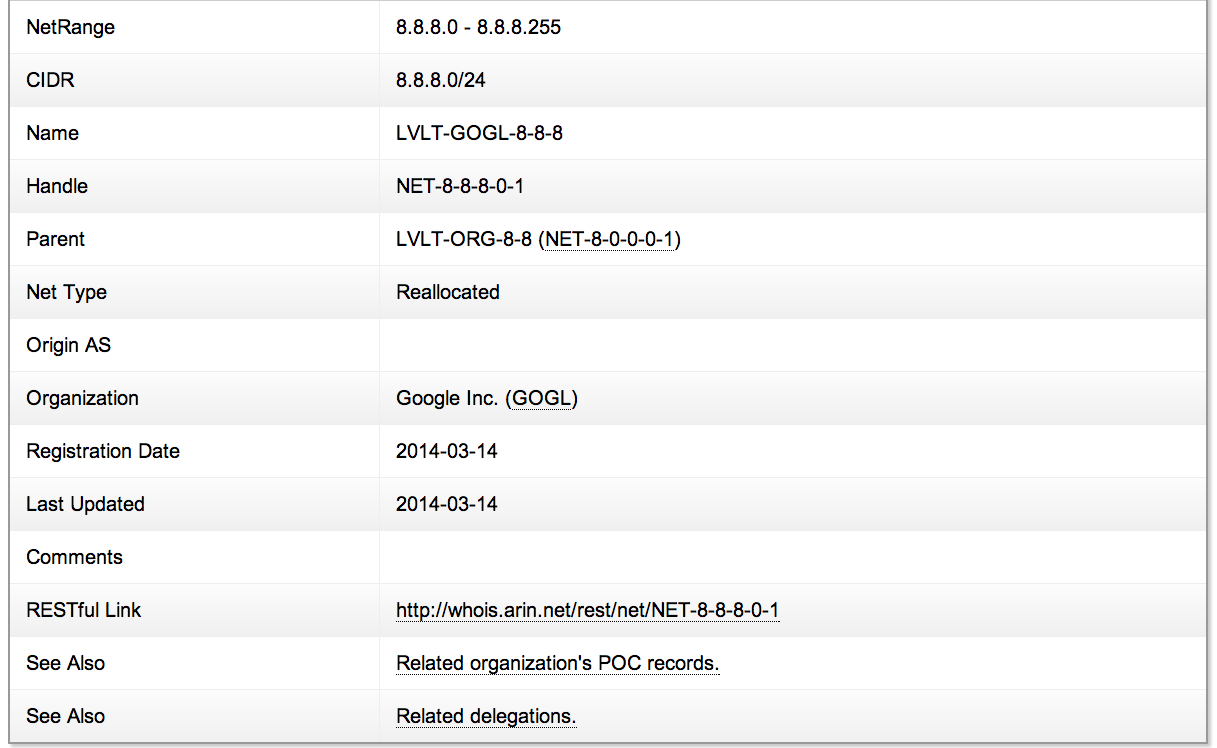
- 8.8.8.8 is Google DNS Server
- whois.iana.org - www.nctu.edu.tw
- Screen Dumps & Explanations
- Select a domain name. Use nslookup to dump its DNS records. Show your screen dump and explain.
- Screen Dumps & Explanations
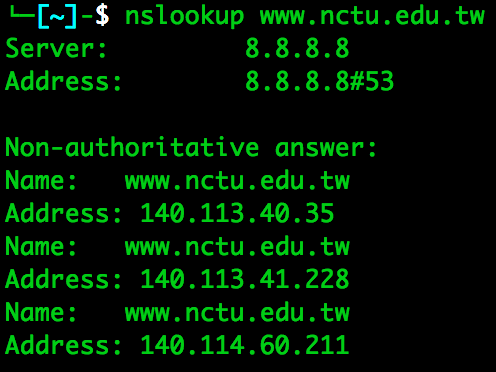
- The http://www.nctu.edu.tw has three IP for load balancing.
- Screen Dumps & Explanations
- Select a domain name. Use traceroute or similar tools to find the access path to that domain. Show your screen dump and explain.
- Screen Dumps & Explanations
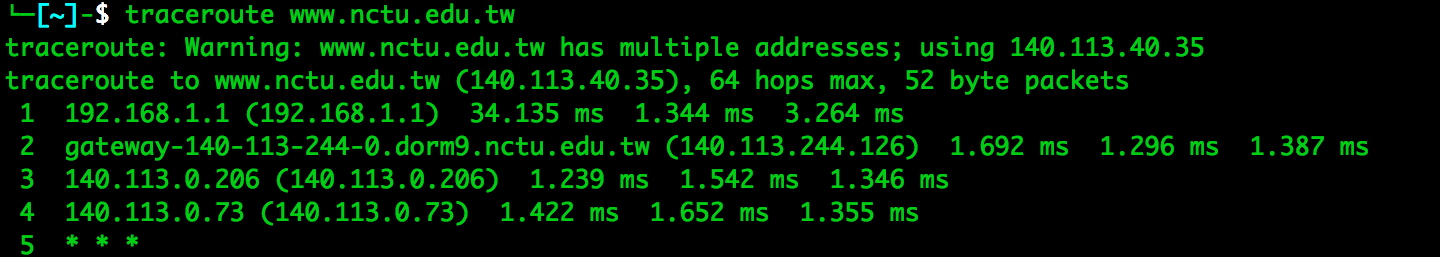
- The destination server seems close the ICMP, so traceroute didn't get the 5th hop ICMP "time exceeded" signal.
- Screen Dumps & Explanations
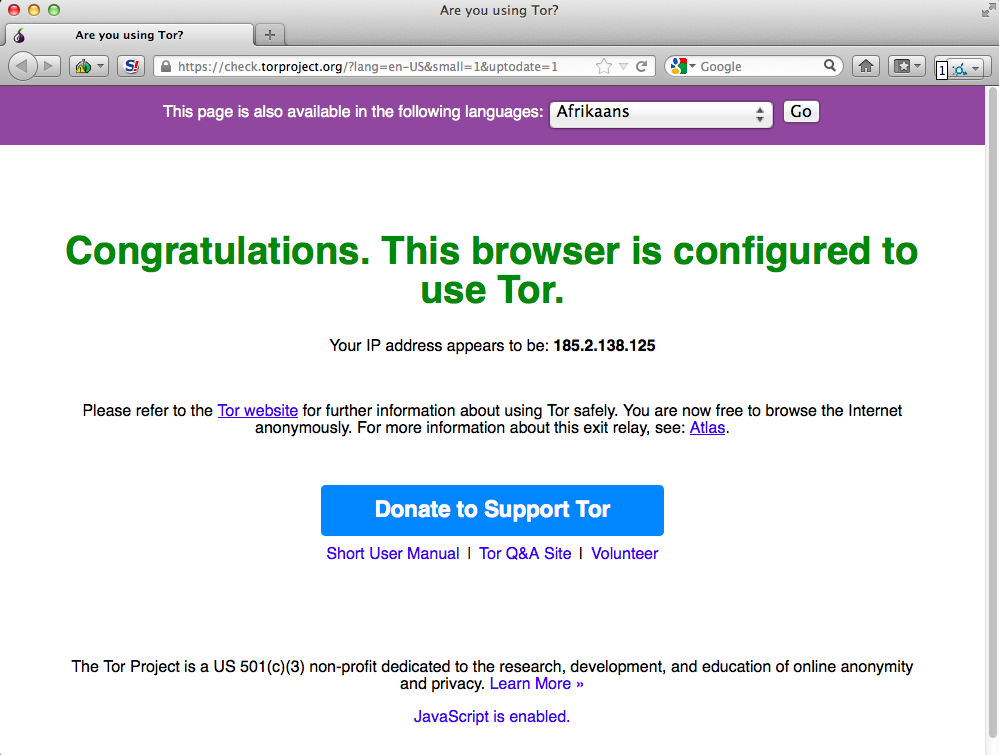
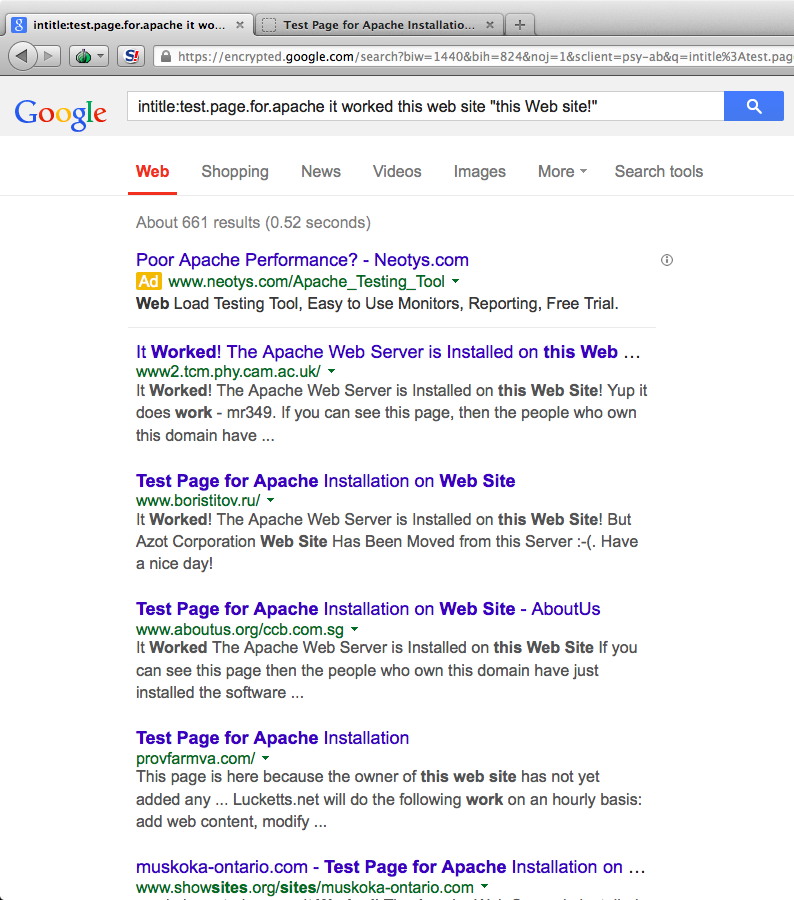
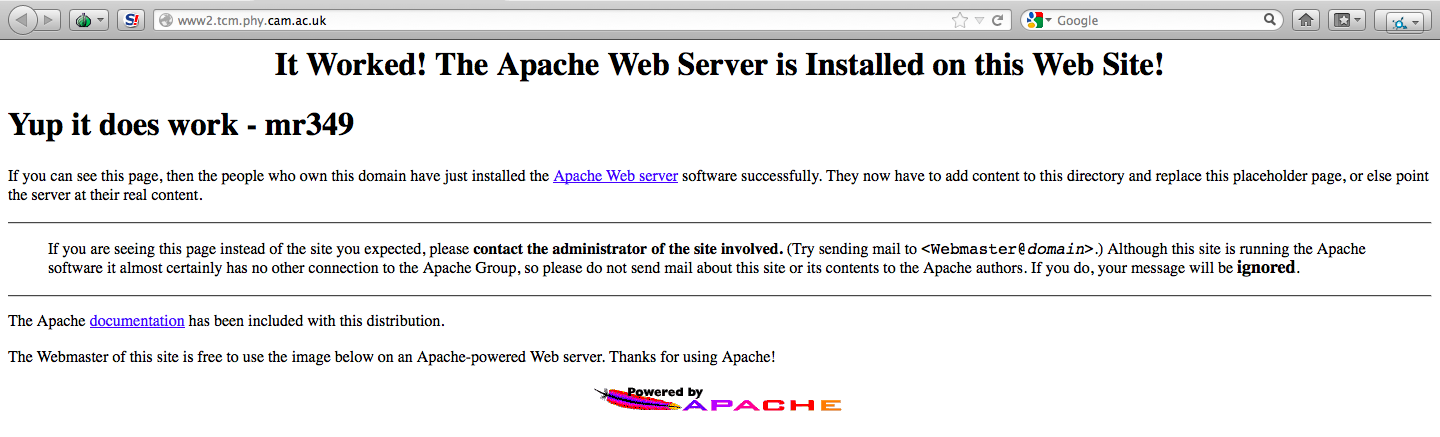
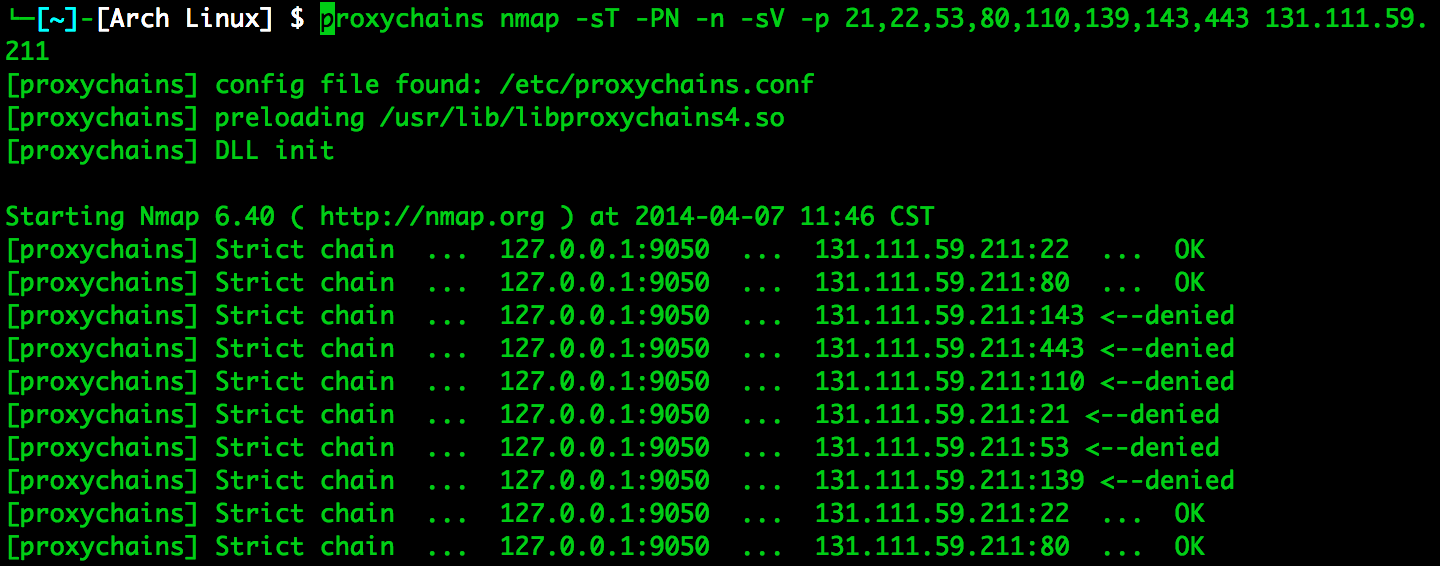
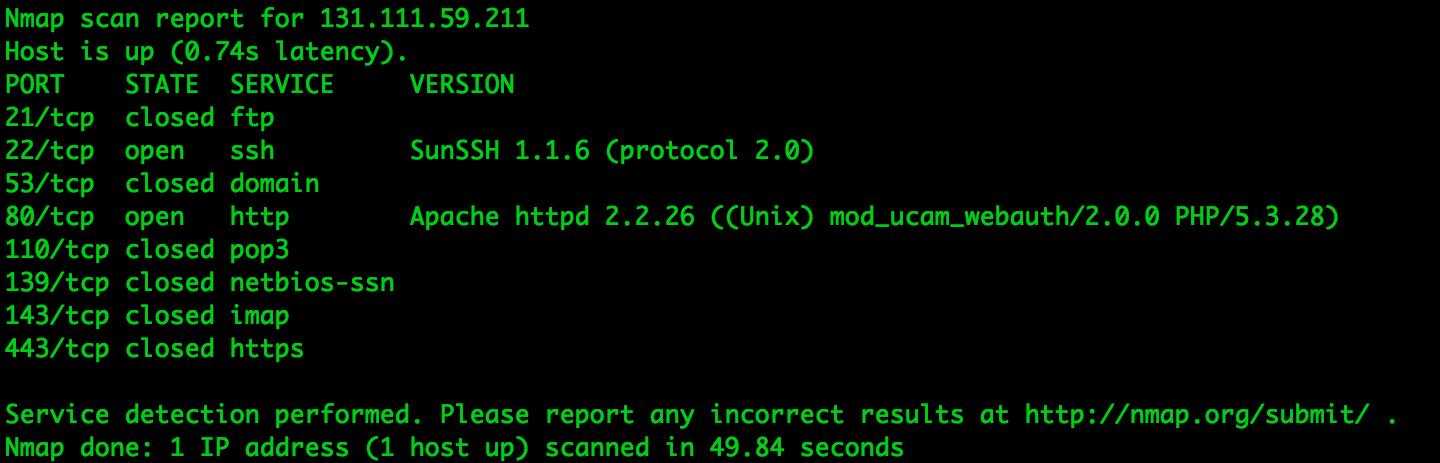
- Follow the case study right before chapter 1. Select one target and run through all tools (Tor, Vidalia, Privoxy, tor-resolve, proxychains, Nmap, socat, nc). Screen dump the process and explain what you got in your screen.
- Screen Dumps & Explanations
- turn on vidalia
- using tor
- finding target
- found target
- used tor-resolve to get target ip
- using proxychains and nmap
- using socat
- get target informations
- turn on vidalia
- Screen Dumps & Explanations
Share
Donation
如果覺得這篇文章對你有幫助, 除了留言讓我知道外, 或許也可以考慮請我喝杯咖啡, 不論金額多寡我都會非常感激且能鼓勵我繼續寫出對你有幫助的文章。
If this blog post happens to be helpful to you, besides of leaving a reply, you may consider buy me a cup of coffee to support me. It would help me write more articles helpful to you in the future and I would really appreciate it.
Related Posts
- HITCON CTF 2015 Quals Write-up
- 新增幾項設定來防範 Clickjacking Frame Attack
- ITC Hw2
- Y2017W32
- MySQL client 預設允許 MySQL Server 讀取本地端的檔案